Overview of Soft AP
Many IoT devices do not offer an interface (display, keypad) to configure them to the local network. Additionally, some products need remote connectivity (permanent or temporary) but cannot do so as a standalone device. This is where Soft AP, or Software Enabled Access Point, comes in. Through software, SoftAP allows a given Wi-Fi enabled device to function like an access point, without the need for special hardware. Below are two examples of how SoftAP is used, how it works, and some of the benefits it provides. There are also some limitations to this functionality that need to be considered before enabling it in an application.
IoT Device Provisioning
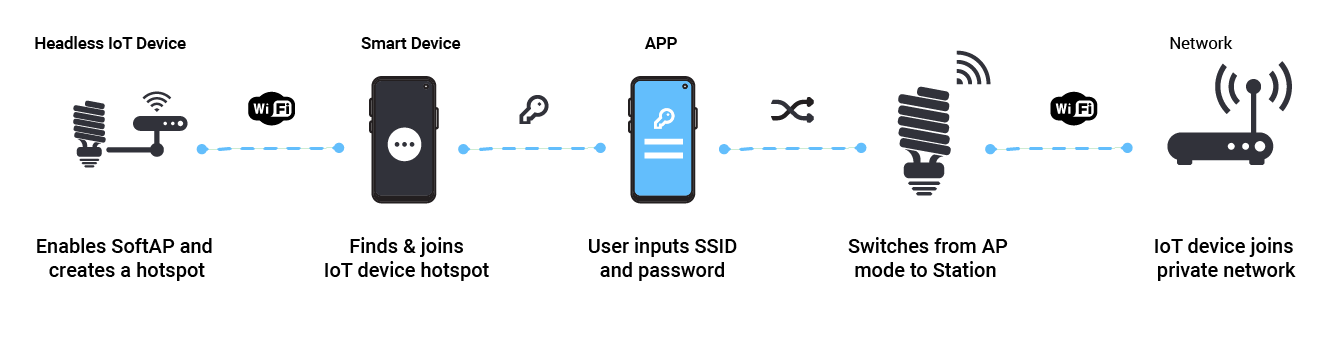
If a headless device needs to connect to a network, it can leverage SoftAP to join it. Here are the general steps taken in establishing that connection:
- The headless device turns itself into a Wi-Fi hotspot by enabling SoftAP
- Using a product-specific app on a smart device, the Android or iOS operating system connects to the SoftAP hotspot automatically or
- The app asks the user for the given private Wi-Fi network name (SSID) and passkey which is entered by the user
- The app sends the SSID and passkey to the headless device over the SoftAP connection
- The headless device drops off the SoftAP network and joins the given private Wi-Fi network
Network Connectivity
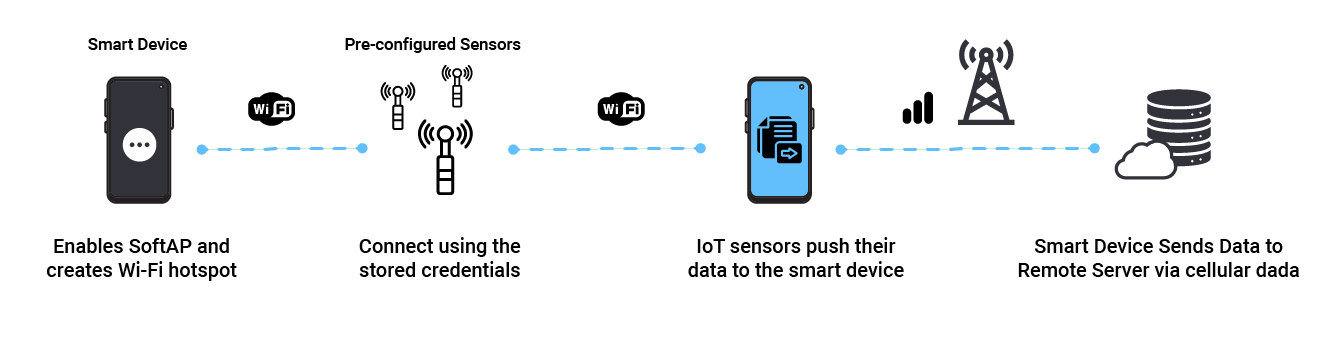
This is simply your mobile phone hotspot, but in an IoT setting and application. For example, there might be a set of sensors that occasionally need to push data to a remote server. The sensors may have Wi-Fi, but there’s no fixed AP infrastructure within range to establish a link. However, there is an occasional Smart Device nearby that has both Wi-Fi and cellular. In this case, the Smart Device can enable its Soft AP mode, and the sensors can connect temporarily to pass along their data for the Smart Device to send it over a cellular network to the end server.
Benefits of SoftAP
- Cost: No special hardware or infrastructure needs to be installed. Instead, it leverages existing hardware like laptops, smart phones, tablets, and IoT devices.
- Simple Set-up: SoftAP functionality is already built into modern operating systems like Linux, Android, and iOS. Simply enable the feature through the network settings or specific software tools.
- Mobile: Since the hotspot is in the Smart Phone, IoT Device, or Laptop, the SoftAP functionality goes where the mobile devices go, thus allowing the ability to set-up networks in different locations.
- Small Size Networks: For networks with fewer devices, SoftAP might be more than enough to manage the connectivity needs, especially if it’s a temporary network, sharing access is acceptable, or the capacity demands are minimal.
- Direct Access: For service technicians, this allows them to access the IoT device directly, without having to go through network infrastructure. Avoids hassle and concerns over infrastructure access and security.
Limitations and Considerations
- Network Size: SoftAP is not capable of managing and supporting a large number of devices, especially if the end devices that are connecting have large demand.
- Performance: Since the device needs to manage its own network connection and those connecting to it, the overall performance of the SoftAP device will degrade and be less than what a dedicated AP could achieve.
- Set-up Risk: Manual input of the SSID and Passcode may be troublesome for non-technical users.
- Security: There may be limited or reduced security depending on the implementation.
- Simultaneous Operation If the SoftAP device can only operate in an either-or mode, this will require the device to switch between SoftAP and STA mode, thus limiting its functionality and performance.
- OS and APP: Due to differences in iOS and Android, as well as Smart Phone software versions and different models, there could be potential issues during the SoftAP set-up process.
Most of CEL’s devices offer SoftAP functionality. Please contact CEL for details or to have a deeper conversation on how we can assist your needs.




